Selecting the Right Residual
Current Circuit Breaker
In every protection system, RCCBs are essential. When the system leaks a substantial current to earth, an amperometric protection mechanism called an RCCB trips. It is crucial to do this since failing insulation could result in fires that could endanger both people and your equipment.
This device continually computes the vector sum of the single-phase or three-phase system line currents and permits the supply of power when the sum is equal to zero. If the total surpasses a value established in accordance with the device's sensitivity, this supply is abruptly stopped. Only current leaking to ground can trigger an RCCB. They must be used in series with an MCB or fuse to safeguard them from any overcurrent’s' possibly harmful thermal and dynamic stresses.
Constrution Characteristics of ABB's RCCB
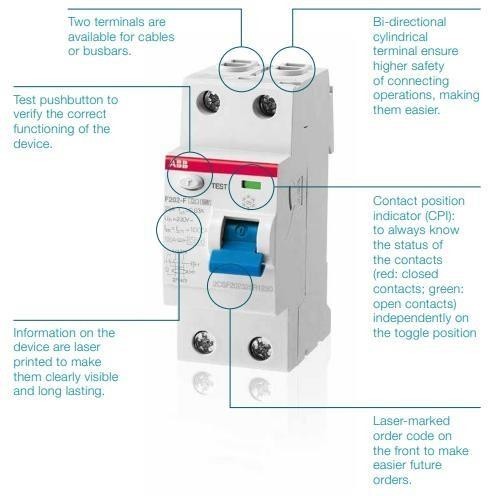
Principle behind RCCB- RCCB works on the principle of Kirchhoff’s law, which states that the incoming current must be equal to the outgoing current in a circuit. RCCB thus compares the difference in current values between live and neutral wires. Ideally, the current flowing to the circuit from the live wire should be the same as that flowing through the neutral wire.
These components are utilised in systems that already have MCBs, which ideally limit the amount of energy passing through and serve as the primary disconnect switches upstream of any derived MCBs (e.g.: domestic consumer unit).
RCCB’s can be classed according to four parameters:
- type of construction
- detectable wave form
- tripping sensitivity
- tripping time
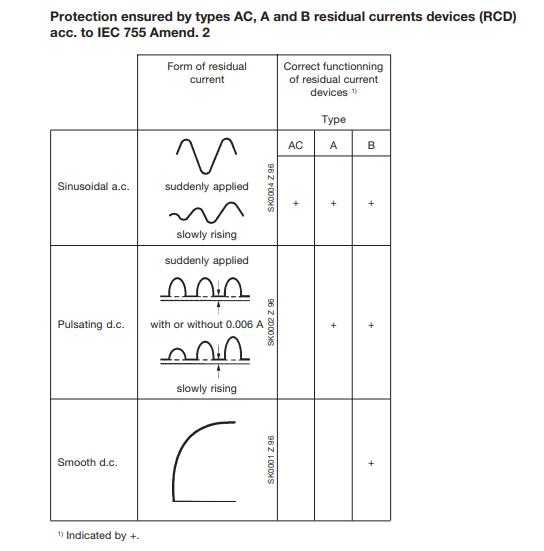
According to the wave form of the earth leakage currents they are sensitive to, the RCCB’s may be classed as:
- AC type (for alternating current only)
- A type (for alternating and/or pulsating current with DC components)
- B type (for
alternating and/or pulsating current with DC components and continuous
fault current).
- Provides protection against earth fault as well as any leakage current
- Automatically disconnects the circuit when the rated sensitivity is exceeded
- Offers possibility of dual termination both for cable and bus-bar connections
- Offers protection against voltage fluctuation as it includes a filtering device that guards against transient voltage levels
- RCCB does not guarantee to operate if none standard waveforms are generated by loads. It’s mainly because RCCB is designed to operate on normal supply waveforms.
- There might be some unwanted tripping of RCCB. It’s mainly because whenever there are sudden changes in electrical load, there can be small current flow to earth especially in the old appliances.
- RCCB does not protect from current overload. It has been designed to protect only when the live current and neutral current are different. However, a current overload cannot be detected.
- RCCB does not protect against line-neutral shocks. It’s mainly because current in them is balanced. The current gets balanced as both terminals are held together.
- RCCB does not protect from the overheating that strike if conductors are not properly screwed into terminals.
AC type RCCBs are suitable for all systems where users have sinusoidal earth current. They are not sensitive to impulsive leakage currents up to a peak of 250 A (8/20 wave form) such as those which may occur due to overlapping voltage impulses on the mains (e.g.: insertion of fluorescent bulbs, X-ray equipment, data processing systems and SCR controls).
RCCBs of the A type are impervious to impulsive currents up to a peak of 250 A (8/20 wave shape). They are especially well suited for protecting systems where the user equipment has electronic devices for rectifying the current or phase cutting adjustment of a physical quantity (speed, temperature, light intensity, etc.) supplied directly from the mains without the use of transformers and insulated in class I. (class II is, by definition, free of faults to earth). These gadgets are capable of producing a pulsing fault current using DC components that the A type RCCB can detect.
B type RCCBs are recommended for use with drives and inverters for supplying motors for pumps, lifts, textile machines, machine tools, etc., since they recognize a continuous fault current with a low level ripple.
Classification of RCCB
RCCB are of two types; the 2 Pole RCCB and 4 Pole RCCB.
2 Pole RCCB:
This is used in case of a single-phase supply connection that has only a live and a neutral wire.
4 Pole RCCB:
This is used in case of a three-phase supply connection.
Rating from 16 Amp ….125 Amp
Sensitivity 30mA, 100mA, 300mA, 500mA and 1A
Benefits of RCCB
Limitations of RCCB
While RCCB has many advantages, it has some limitations as well:
Residual current sensitivity and environment
Household and special environments In to 30 mA
High-sensitivity or physiologically sensitive RCCB
IEC/EN 60364 makes the use of these devices mandatory in all bathrooms, showers and private and public swimming pools and environments in which plugs and sockets may be installed without insulating or low safety voltage transformers
Laboratories, service industry and small industry In from 30 mA to 500 mA
Large service industry and industrial complex In from 500 mA to 1000 mA
Complete range of ABB RCCB available at AMT Electric
Source: ABB Data Manuals